
Native to the region now known as Iran and Iraq, pomegranate has been cultivated since ancient times, finding its way into our ancient stories and mythos, such as the Greek myth of Persephone. The fruit symbolizes prosperity in Ancient Egypt, and fertility in many other cultures, including China, Armenia, Iran, and Ancient Persia. Some Jewish scholars even believe that it was a pomegranate, and not an apple, that lead to the banishment of Adam and Eve from the Garden of Eden.
Dried pomegranates are very rich in Vitamins B6, C, E, and K, as well as minerals such as phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and magnesium, as well as antioxidants that can help your body repair cells and boost your immune system. Purchasable from any good fruits and vegetables retailer, it will give a sweet, tangy flavor when added to your favorite dishes, as well as an ingredient in foods such as jellies, sauces, soups, baked apples, and flavorful cakes. Pomegranate seeds can also be dried and be used in Indian and Pakistani cuisine as a spice. When ground, they can be used to quickly thicken curry sauce, as well as a preservative agent.
The fruit can be enjoyed fresh or dried, but most experts agree that it is better to consume it dried, as the dehydration process concentrates the nutrients in the fruit. Shoppers should be aware and only purchase dried pomegranate with an approval label by the medical council. Although it is found in many other regions of the world, it is very common in Indian markets.
Dried pomegranates can also be used for decorative purposes. In India, many people mix it with other dried fruits, such as apples and perricone, as well as dried nuts to decorate their houses. Medically, dried pomegranate can be used as weight loss prevention, skin care, cancer prevention, cure for the common cold, immune system booster, coronary artery diseases, wrinkles, hemodialysis for kidney disease, burns, and infant brain injury.
Explore Articles
 Enriched Dried Pomegranate
Enriched Dried PomegranateThe luscious fruit Pomegranate is native to the region of Armenia , Persia named as Iraq nowadays and the western Himalayan range. But now...
 Dried Pomegranates in everyday food around the world
Dried Pomegranates in everyday food around the worldDried pomegranates are a health food and have been found time and again to be enriched with vital nutrients. It is mentioned in scriptures...
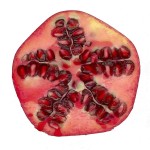 Dried Pomegranates and Online Purchase
Dried Pomegranates and Online PurchaseDried Pomegranate is a great fruit derived from fresh pomegranates. If dehydrated appropriately, the nutrients inside the dried pomegranate can be preserved. Therefore, consuming...
 More Information about Dried Pomegranates
More Information about Dried PomegranatesPomegranate is a super fruit for all occasions, they form an integral part of festivities, get together with family and friends, and fruit salads...
